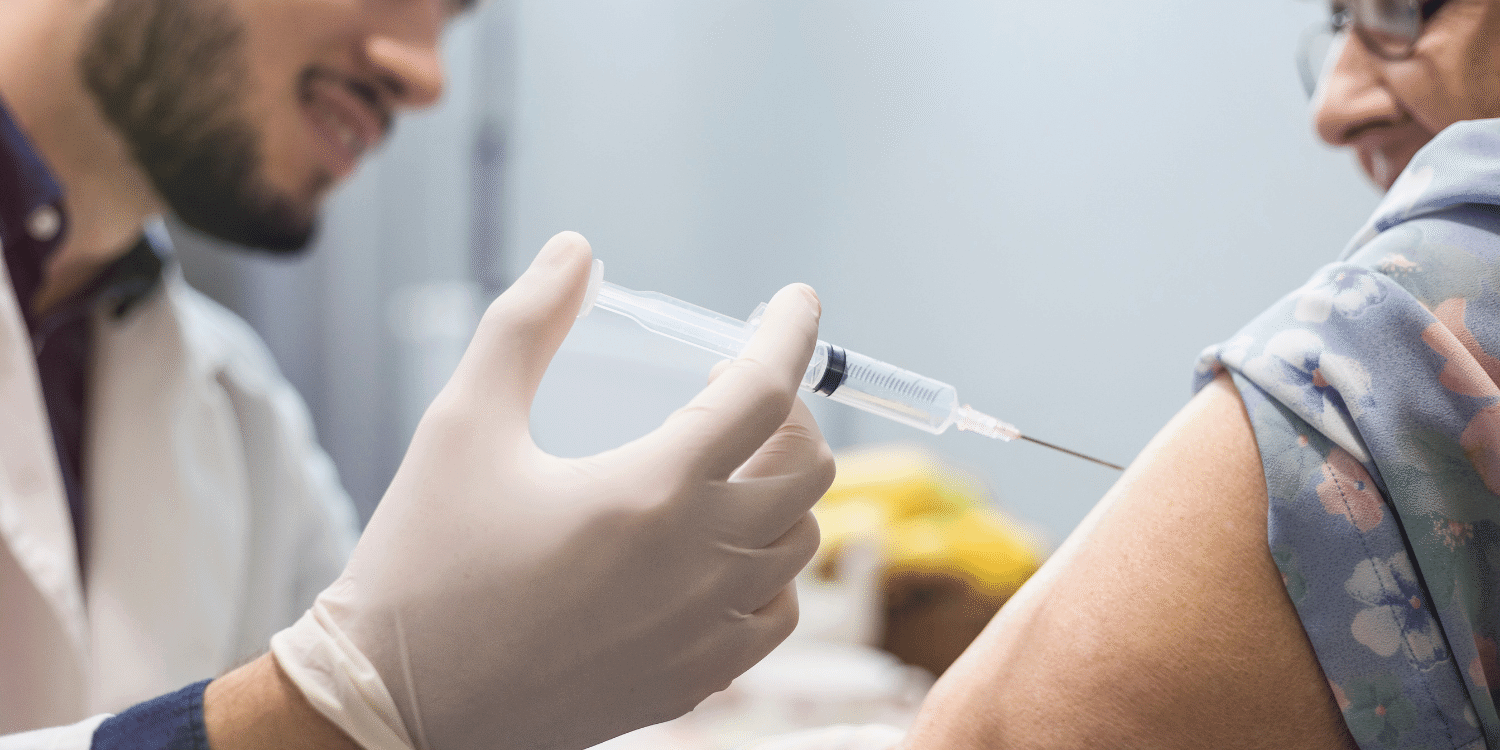
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis
Ticks form the majority of the animal group “arachnids”. A tick needs much more blood for nutrition than other parasites. If an attached tick remains unnoticed, it can suck blood for a period of 15 days. Hard ticks are known to be the most widespread type of ticks in Lithuania, and can be found almost in all parks and forests.
When a tick sucks your blood, it transmits bacteria that cause severe disorders such as tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme disease, and Ehrlichiosis.
The tick-borne encephalitis represents the most dangerous disease. The death rate from the disease reaches 0.5 to 1% of the infected. One-third of people never make a full recovery after tick-borne encephalitis. The most common residual effects include psychoneurological symptoms such as inability to concentrate, sleeping disorders, chronic headache, increased sensitivity, behavioural changes, and more rarely, paralysis.
A person who gets infected with tick-borne encephalitis virus, two or three days after a tick bite can develop flu-like symptoms such as a headache, fever, and dull pain in the body. These symptoms last for about a week. Afterwards, the majority of people feel better. In one out of three cases this virus can spread through the organism and even reach the brain lining, and the brain itself. The second stage of the tick-borne encephalitis can be marked with a fever, severe headache, vomiting, faintness, chilly sensation, stiff neck, and loss of consciousness. If the listed symptoms develop, immediately seek medical advice.
There is no specific treatment, i.e. treatment against the infectious agent. A person can only receive treatment to relieve symptoms, i.e. a drug therapy for symptomatic relief.
Vaccination is the most effective measure against a tick-borne encephalitis. The effectiveness of the vaccine against tick-borne encephalitis reaches 98%.
Standard vaccination plan:
- the first dose;
- the second dose (1-3 months after the first vaccination);
- third dose (5-12 months after the second dose).
Accelerated vaccination plan:
- the first dose;
- the second dose (2 weeks after the first dose);
- the third dose (5-12 months after the second dose).