Is foot deformation a cosmetic problem or it does affect overall health?

Are high heels – the symbol of elegance – the main contributing factor to foot problems?
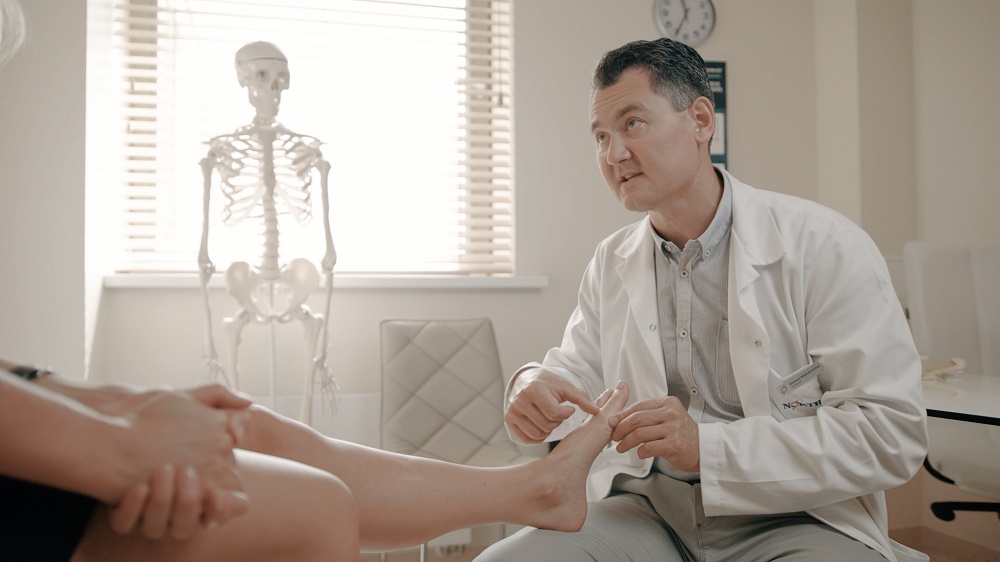
According to historical sources, people used to wear high heels in the 9th century in the Persian Empire. Horse riders wore high heels in order to balance their feet in the stirrups, and to keep stable when horse riding. During World War II, women used to put on high heels as one of the ‘means’ to emphasise their femininity. Since then, high heels have become an inescapable symbol of female elegance and grace. But can wearing high heels actually cause serious foot problems? Let’s discuss it with Aleksas Makulavičius, orthopaedist and trauma specialist at Northway Medical Centre.
Doctor, tell us: can women’s favourite high heels lead to irrevocable feet deformities?
Although many people think that toes become deformed due to wearing high heels too often, there is only some truth in this. In fact, this deformity is usually inherited. Around 80% of patients say that their family members (mother, grandmother or any other relatives) had the same problem.
But external factors, such as wearing shoes that are too tight or too high, and especially wearing them for a long time, can definitely deform healthy feet. According to statistics, there are far more feet and toe deformations in countries where people wear shoes. For example, Japanese had fewer feet deformations until the European tradition of wearing shoes emerged in Japan.
Feet deformities and abnormalities are related to the weakness of muscles and ligaments and disorders in their function. Sometimes frequent pregnancies can also affect the feet. If a woman gains weight, her increased body mass may contribute to the loosening of ligaments and cause feet deformities.
Feet deformities are more common in women than in men. Women develop feet abnormalities and deformities ten times more than men do.
What are the most common types of foot concern?
The most common foot problems are related to deformity of the toes. Around one-third of people have this problem. Foot deformities are common in women. A hallux valgus deformity, commonly called a bunion, is the commonest forefoot deformity in women.
Which symptoms indicate that you need medical advice?
First of all, foot deformations are visible. If the deformity was minor but later developed, you will see it with your own eyes. If you happen to see some changes in the shape of your foot or feel discomfort and tiredness, you should see your GP because these signs can be the first symptoms of development. It is critically important to see your doctor before your joints wear off. The worst thing happens when certain foot deformities and incorrect loading on foot joints cause joint wear off and degeneration. In this case, medical specialists have limited options and need to stabilise the damaged joints.
Is foot deformation a cosmetic problem or it does affect overall health?
It is more than just a cosmetic problem. First of all, it is an orthopaedic problem because plantar toe joints wear off more quickly and cause pain in the feet. Our feet are a small body segment which supports our body and bears its weight, so when we lift our feet, the loading force is very high. Often people don’t even have a clue about the actual load affecting their feet. The sooner you see your doctor after the onset of initial feet deformity symptoms, the less complicated the treatment and the faster recovery will be.
What type of work – sedentary or standing – affects the feet more? Can intense physical activity help avoid feet deformities?
Both long-term sedentary and standing work have a negative impact. We need balance in life.
Human beings were made to move. For this reason, physical activity is one of the crucial elements of a healthy lifestyle. Depending on physical capability and fitness level, each of us needs physical activity and exercise for optimal body development, normal performance of internal systems, comprehensive health and the ability to work. Insufficient physical activity will cause a person to be weaker and will require a lot to satisfy their social and biological needs. And our feet are no exception to this. Joints must move. Reasonable physical activity is a prevention method against all possible joint diseases.
Stretching also plays an important role. Sitting for a long time shortens certain muscle groups. When muscles do not get resistance, they shorten in length so our body gets overloaded, and we can feel this while moving.
What advice do you have for people with foot deformity?
The most important piece of advice is to take care of your feet, keep them healthy and avoid wearing ill-fitting and uncomfortable shoes. Remember that our feet support our body and bear its weight. My advice is to carefully choose comfortable, well-fitted shoes with a heel that is 2-3 cm in height and roomy at the front. I would also recommend avoiding wearing high heels or not wearing them frequently or for longer periods of time. When you wear high heels, you lose your foothold and this increases the load on your toes. Over time, this process leads to distortion of the big toe. This is why it is advisable to wear high heels only in exceptional cases. If your job involves standing all day (for example if you’re a hairdresser, salesperson…), you should particularly avoid wearing high heels. Another important thing is that our feet are also affected by flat-soled shoes, shoes with firm soles and no shape, and high and hard platforms.
Foot stretching, including flexion exercises and toe contractions, must form part of your daily routine. In summer, go barefoot to have a good massage therapy for your foot.
Pregnant women are advised to wear special compression socks and use supportive insoles which strengthen the feet, silicone braces or another product from a wide range of orthopaedic products available on the market. All of these measures listed will be helpful only if you don’t feel any pain or discomfort.
How do you decide whether surgery is necessary?
Any surgical intervention comes with some risk, so this risk must be carefully assessed. You should consider having surgery only when pain in your feet worsens your daily life. The pain occurs not only because of the bunion rubbing against an uncomfortable shoe or callosity, but in the feet itself after walking. Annoying pain indicates that you need treatment and should not delay your visit to the GP. Arrange a visit to undergo an uncomplicated procedure and obtain good results.
What does surgery involve?
The surgeon chooses the surgery technique depending on the patient’s age, grade of deformity and bone structure. The surgery involves both a bone repair and correction of tissues surrounding the affected area. The surgery is conducted under intravenous anaesthesia. It takes about an hour.
What is the course of the procedure? When can you return to work and your daily routine?
Modern surgery is comfortable enough. The patient will experience minor post-operative pain for 1 or 2 days, but they can take any painkillers. If the deformity is minor, the post-operative period usually lasts around a month. Usually, people who work in an office can return to work in about 5 weeks.
You can rest only on the ankle during the recovery period. You can also use special post-operative shoes designed for comfortable and safe walking after surgery. During recovery, you must not only put your leg into a correct position but also follow all other instructions from your surgeon – otherwise you will jeopardise the success of your surgery.
Physical load on your foot after surgery must be restored gradually. You will need to do physical therapy and specific exercises. The recovery period also depends on the patient’s personal awareness and spirits.
What are the results of the surgery? Can a deformity renew?
Typically, surgery has a successful outcome. If surgical management has been properly performed, the probability of deformity renewal is around 5%.
If the surgery is performed on a child whose musculoskeletal system has yet not developed, the probability will be higher. For this reason, only adults are advised to have surgery.