Neurological disorders
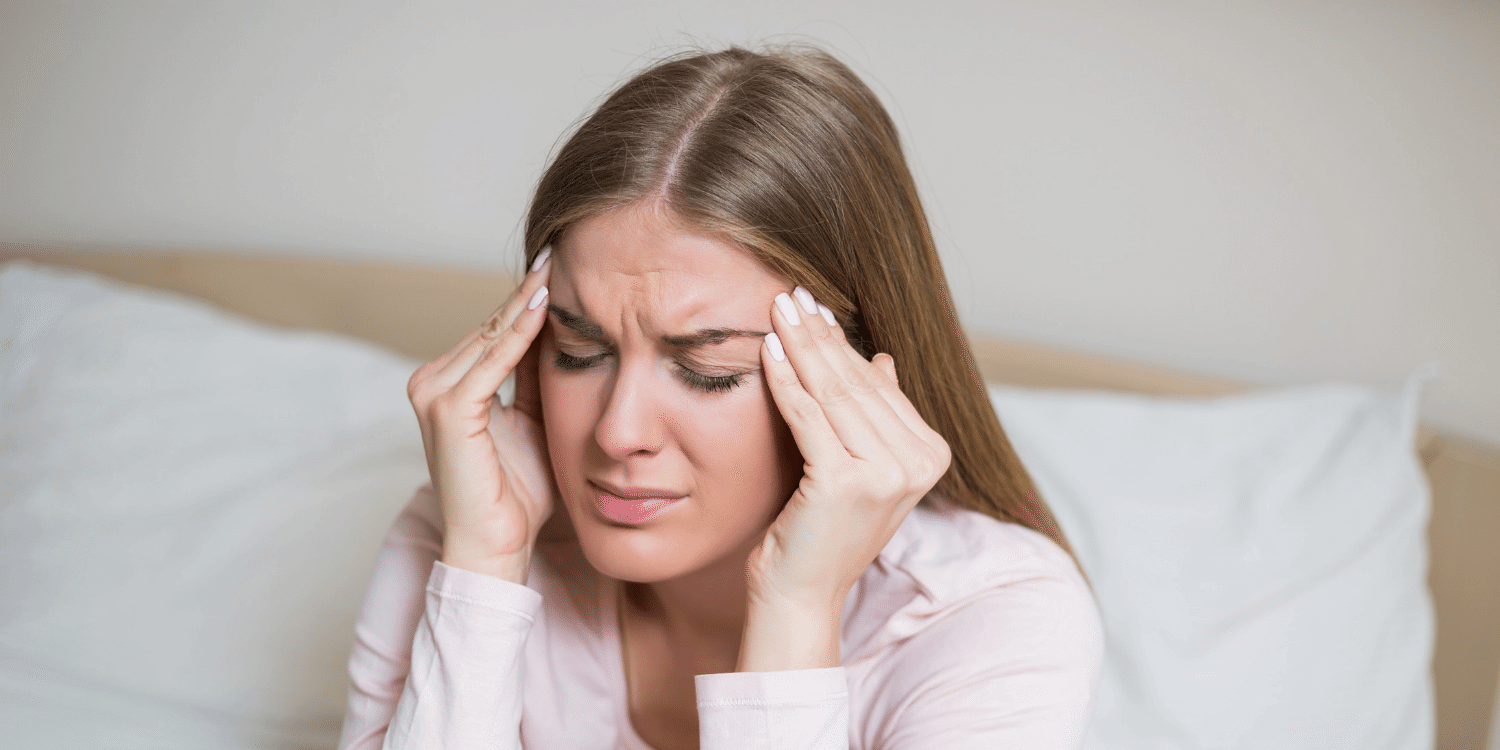

Migraine is a condition characterised by episodic headaches that last from 4 to 72 hours and are followed by various neurological digestive disorders, including disturbances of the autonomous (vegetative) nervous system. Migraine’s origin is neurological, i.e. it occurs due to changes in the nervous system. The first signs of migraine include a feeling of uncertainty, yawning, tiredness, constrained neck, thirst, increased sensitivity to light and noise, irritation, and craving for desserts. A migraine aura (additional neurological symptoms) can occur. Neurological symptoms occurring prior to migraine include disturbance of vision, limbs oedema, and weakness.
Epilepsy is a chronic brain disease characterised by recurring spasms causing temporary disturbances of consciousness, motor activity, sensation, or mental activity. Possible causes of epilepsy include heredity, imbalance of certain chemical substances in the organism, brain traumas, poisoning with certain chemical substances, bad habits (alcohol, drug abuse), an insult, infant trauma during labour, brain tumours, and inflammation.
Encephalitis is a condition characterised by inflammation of the brain, spinal cord, and their membranes. It comes on abruptly and develops rapidly starting from fever, headache, fainting, weakness, nausea, sleep disturbances, loss of consciousness, paralysis. Encephalitis is caused by viruses and bacteria that are usually transmitted by mites (tick-borne encephalitis). Viruses can also enter the body by contact with infected cows or goat milk or occur as a complication of flu, rheumatism, typhus or other diseases. It some cases, it is impossible to cure this disease and it can cause disability for life.Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive degenerative disease of the nervous system characterised by the impairment of cognitive functions, passivity in daily life, behavioural changes, and neuropsychiatric symptoms. Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia (disturbance of thinking). The causes of this disease remain unknown, therefore, there are no direct treatment methods – only medicines which can improve the patient‘s condition (memory and special orientation). The main symptoms of Alzheimer’s include impairment of short-term memory, loss of speech, loss of ability to make fine movements, disturbance of cognitive functions.